Usefull operations¶
Export to json file¶
You can export any design3d objects to a json file. To do so, you can just call the method save_to_file.
Here is an example how you can save a plan face 3d to a .json file:
import design3d
from design3d import surfaces, faces
face = faces.PlaneFace3D.from_surface_rectangular_cut(surfaces.Plane3D(design3d.OXYZ), -1, 1, -1, 1)
face.save_to_file('path/to/where/to/save/your/file.json')
Import from json file¶
If you have a json file containing design3d objects, you can use the method dessia_common.core.DessiaObect.from_json to import it.
Example:
import dessia_common
design3d_object = dessia_common.core.DessiaObject.from_json('path/to/your/file.json')
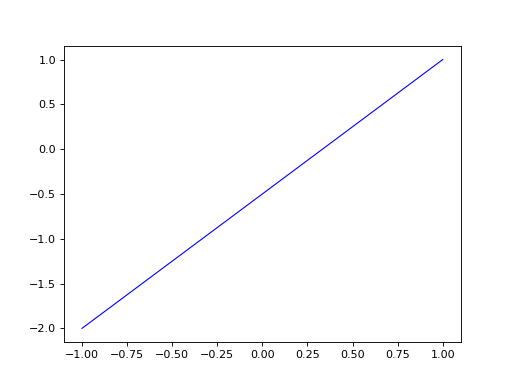
Matplotlib plots¶
To have a matplotlib visualization of a design3d object in 2D or 3D, you can call the plot method in any object. See the following example
import design3d
from design3d import edges
from design3d.core import EdgeStyle
line_segment2d = edges.LineSegment2D(design3d.Point2D(1, 1), design3d.Point2D(-1, -2))
line_segment2d.plot(edge_style=EdgeStyle('b'))
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
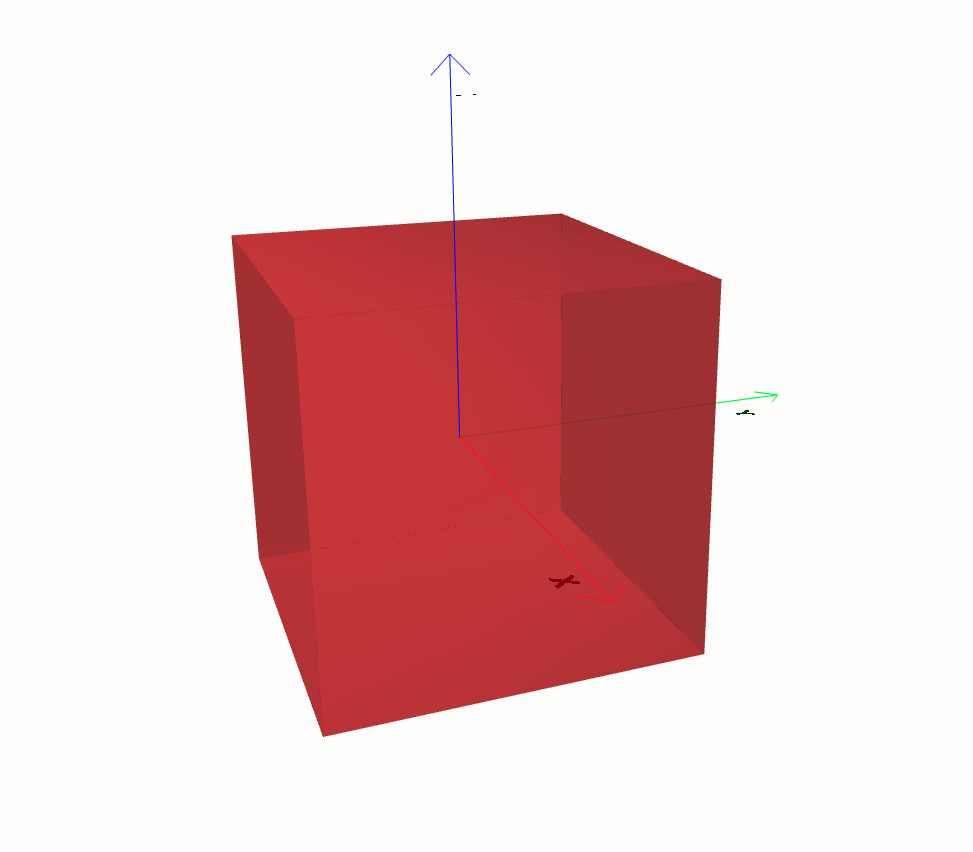
Model Visualization¶
To have a 3D visulaization of your model, most of the 3d objects has a babylonjs() method, which you can use to do so. Babylon.js is an open-source, JavaScript framework and engine for creating and rendering 3D graphics and games in web browsers. Here is an example on how you can do it.
import design3d
from design3d import primitives3d
block = primitives3d.Block(design3d.OXYZ, color=(1, 0.1, 0.1), alpha=0.6)
block.babylonjs()